ISRAMAR SWAN System - Coastal wave forecast
System Decription
SWAN is a third-generation wave model for obtaining realistic estimates of wave
parameters in coastal areas, lakes and estuaries from given wind, bottom and
current conditions. However, SWAN can be used on any scale relevant for
wind-generated surface gravity waves. The model is based on the wave action
balance equation with sources and sinks. The model developed by Delft
University of Technology (Netherlands) and is supported by Office of Naval
Research (USA) and Rijkswaterstaat (as part of the Ministry of Transport, Public
Works and Water Management, The Netherlands). SWAN is a freely available,
open-source model and can be used freely under the terms of the GNU General
Public License.
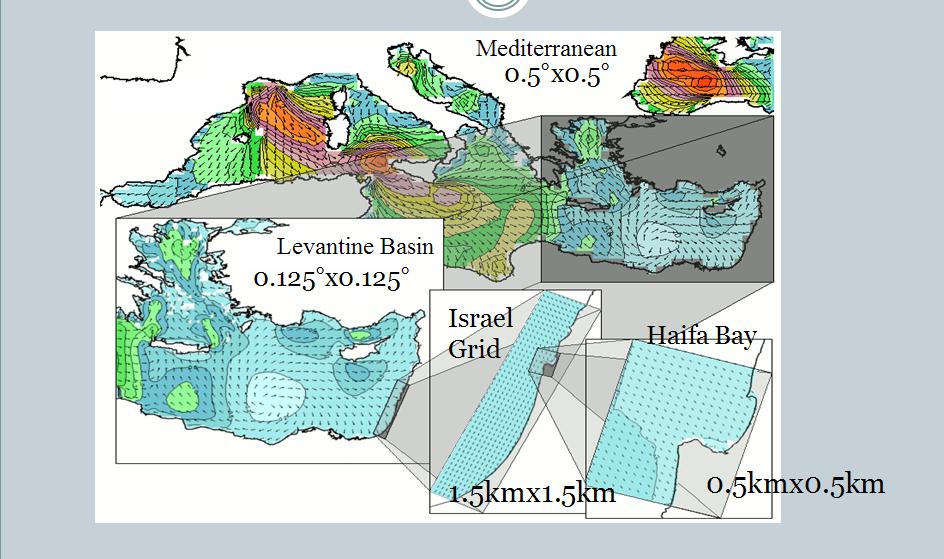
ISRAMAR implementation of SWAN model consists of 4 nested grids (Figure below):
- Mediterranean
- Levatine Basin
- Israel Coast
- Haifa Bay
|
- - resolution of 0.5°x 0.5°
- - resolution of 0.125°x 0.125°
- - resolution of 1.5 km x 1.5 km
- - resolution of 0.5 km x 0.5 km
|
ISRAMAR SWAN system uses wind fields at 10 m above sea surface with
a resolution of 0.05° x 0.05° provided
by The University of Athens's Atmospheric Modeling and Weather Forecasting Group led
by Prof. G. Kallos (Regional meteorological model SKIRON).
SWAN, governed by SKIRON's winds, runs daily on a LINUX workstation, and requires approximately
3.5 hours to produce 72 hours wave forecast for all grids. Graphical
presentation of the forecast is performed by scripts running the visualization
program FERRET.
Go back
|